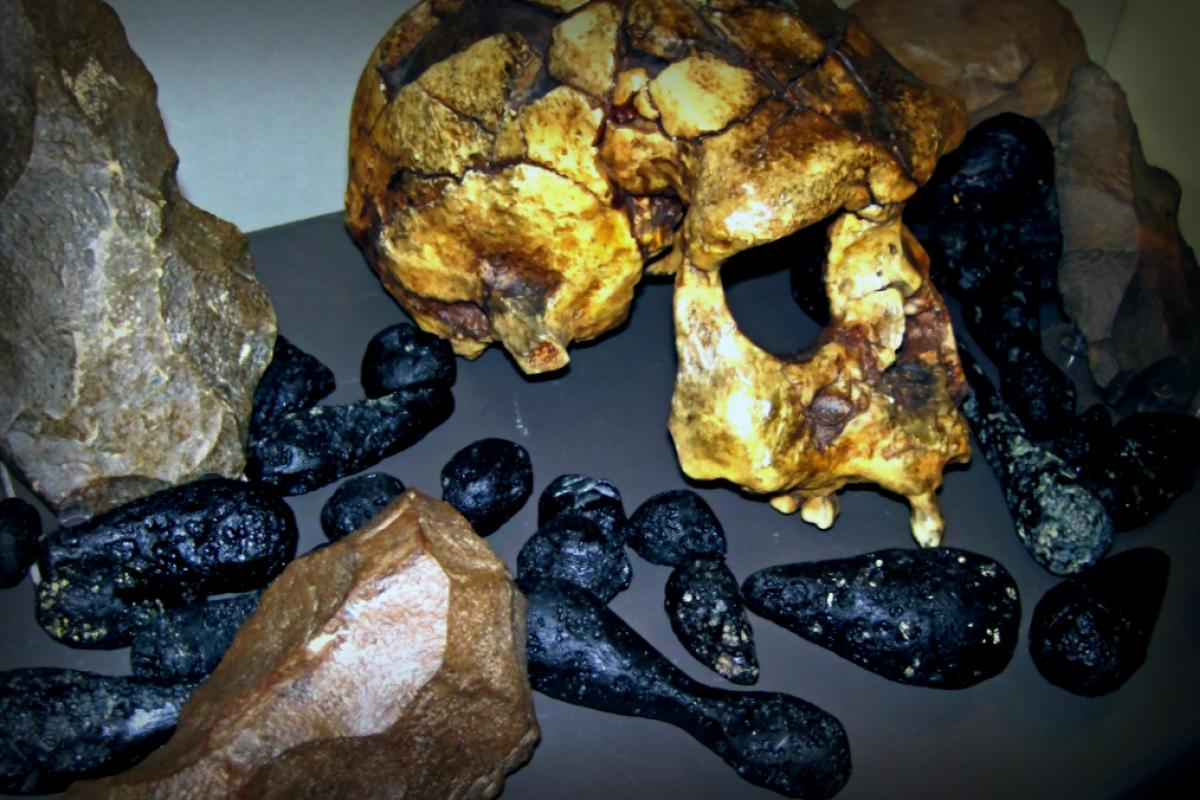
Something pretty wild has just happened in the world of archaeology! The oldest human remains ever found have popped up from the icy depths of Antarctica, sending waves of excitement and confusion through the scientific community. This surprising twist has forced experts to rethink traditional beliefs about how early humans explored tough environments and managed to survive in extreme conditions.
Unearthing the Past

The journey to uncover these ancient bones was anything but easy. A brave team of researchers took on the frosty and remote terrains of Antarctica, battling the harsh climate to unveil this incredible piece of human history. Thanks to the unique circumstances—like the freezing temperatures and untouched landscapes—the remains have been preserved in outstanding condition, piquing interest and curiosity.
Initial examinations suggest these remains are incredibly old, claiming the title of the oldest finds on the continent. In a region normally recognized for its special ice formations and unique wildlife, this significant discovery provides new dimensions to our understanding of human history.
What This Means for Migration Theories

This groundbreaking unearthing showcases profound implications for existing theories surrounding early human migration. The commonly held view suggested that our ancestors didn’t really make it into the brutal Antarctic climate. However, this finding not only counters that idea but encourages us to reconsider how humans adapt to and endure in extremely challenging environments.
Additionally, this discovery opens the door for exciting archaeological pursuits in Antarctica. If early humans could actually survive, maybe there’s more evidence hiding beneath the ice, waiting to be uncovered. The scope for investigation here is immense!
Welcome Skepticism

As always with revelations that shake up established scientific beliefs, skepticism is sure to arise. Some critics are cautioning that these remains might not be as old as suggested, or could stem from modern human activities in the area. This lively debate is a natural part of the scientific process, ensuring that evidence is scrutinized and theories tested.
Consensus within the scientific community takes time, with current discussions revolving around a thorough examination of the finds through various tests.
Diving into Analysis

A variety of science techniques are being utilized to study the remains. Carbon dating will help determine their age, while DNA tests will unlock information about their genetic lineage. The science community is buzzing with anticipation, hoping these outcomes will shed light on our ancient ancestors and how they lived.
Beyond the age and relations, researchers are also diving into other areas—like cultural lifestyle, eating habits, and more. These studies, leveraging techniques such as isotopic analysis, are aimed at making sense of how these early humans managed to thrive in the brutal Antarctic conditions.
Shifting Human History Perspectives

The ramifications of this discovery could be monumental in reshaping our view of human history. If confirmed as the real deal, we’d need to rework some significant portions of what we know about early human migration and survival strategies. This could influence academic circles and curricula alike, enriching our understanding of our past.
The intrigue around the find has also sparked the public’s imagination—much like the buzz around the recent find of Amelia Earhart’s long-lost plane. The thought that our ancestors might have roamed the frigid expanse of Antarctica eons ago is captivating. This finding serves as an exhilarating reminder of the remarkable adaptability and resilience inherent in humanity.