Battery technology often feels like a foreign language to most folks, but it’s essential info for EV enthusiasts and owners. Let’s unpack this and clarify why the details are important. Imagine electricity as a busy city road: the old-style silicon is like a congested street that operates but at the expense of efficiency and heat. On the flip side, silicon carbide (SiC) is like a repaved street that handles more pressure without falling apart. Then there’s gallium nitride (GaN), comparable to a smooth express lane designed for rapid changes—it switches power in a flash and minimizes waste.
Here’s why that’s important: less energy wasted results in lower heat production. This means smaller coolers, steadier power flow, and more of that battery energy translates into actual mileage instead of dissipating as heat. Industry experts predict a strong growth in 2025 for these high-tech power chips, especially as auto manufacturers revamp their inverters, onboard chargers, and DC-DC systems.
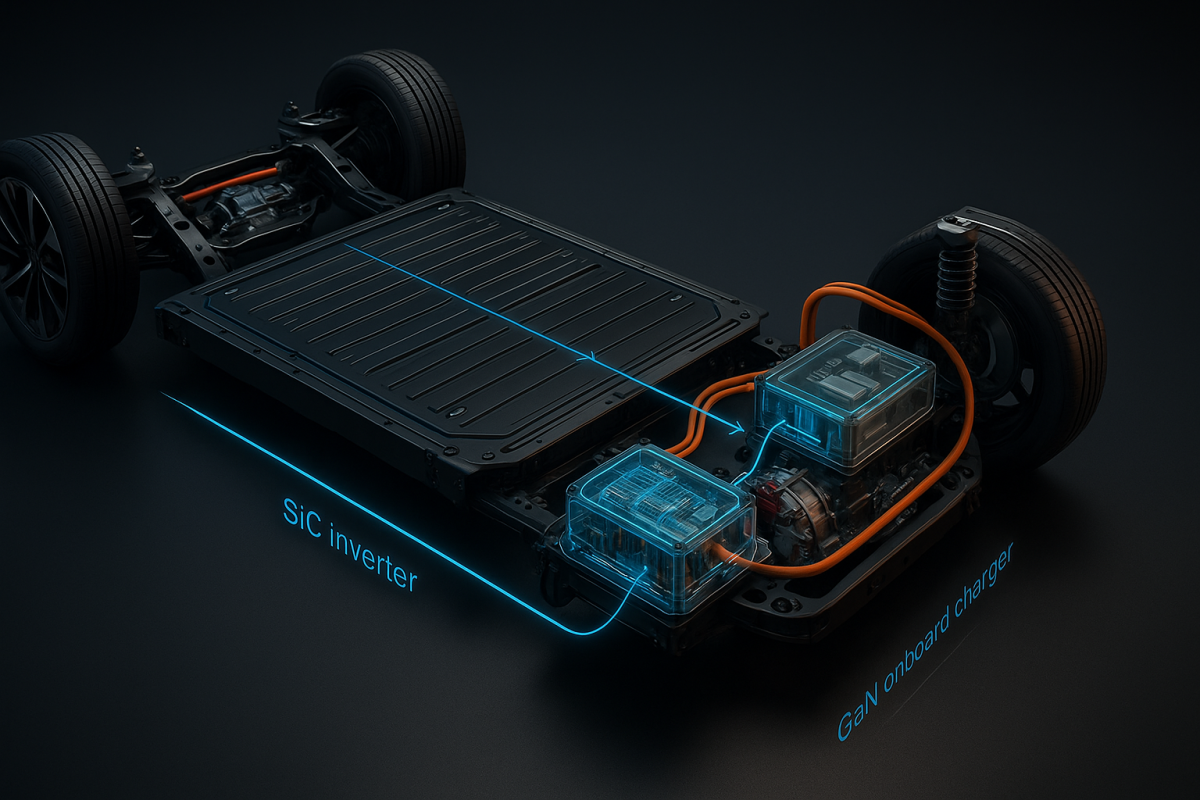
SiC Drives the Motors; GaN Charges Up
Inside every EV, two crucial components play distinct roles. The traction inverter powers the motors during driving—it’s the major player. On modern 800-volt vehicles, silicon carbide (SiC) is the go-to option. Tests conducted by Infineon show impressive efficiency improvements with 800-volt traction inverters versus old-school silicon, leading to more stable driving range and cooler vehicle performance.
SiC remains efficient even under heavy use, which enhances highway range and prevents overheating during those long summer drives. Meanwhile, the onboard charger (OBC), along with some DC-DC hardware, works its magic when you’re plugged in—this is where gallium nitride (GaN) shines. It can handle power transitions so quickly that it allows the charger to be lighter and smaller, saving energy between the wall outlet and battery. Existing designs underscore this potential, including a 6.6-kW automotive GaN onboard charger that reflects both its efficiency and compact design. A comprehensive Texas Instruments reference design details how control strategies are utilized alongside high-frequency switching in a modern GaN onboard charger.
Putting it all together means reduced charge times at the equivalent socket and less heat building up at the front of the vehicle. Automakers cleverly combine the two materials: SiC serves in the primary inverter, while GaN is utilized in the charger—for each to deliver maximum benefit where it counts.
Your Experience on the Road: Quicker Charging and Enhanced Range
So, how does this translate to your driving? A GaN-based charger waste less power, ensuring that more energy gets to the battery. This shortens your charging time at home and means that fast charging can maintain a steady output longer without dropping. With a SiC inverter, less energy is lost as heat during regular driving or acceleration, which increases overall efficiency and allows better performance especially when you’re loaded up or towing. With reduced heat overall, the cooling systems like fans lower their workload, resulting in a quieter and more comfortable drive.
Are the Extra Costs of SiC and GaN Justified?
As of now, SiC components are generally pricier than standard silicon, while GaN chargers are still relatively new to mass production. However, demand is soaring, and these components are being integrated into common vehicle models. The simple truth is, better efficiency means more savings for you—due to less need for larger cooling systems, lighter materials, and less energy wasted on every trip.
Final Thoughts
If a spec sheet mentions SiC for the traction inverter, you can expect a cooler experience and consistent driving range on 800-volt models. Similarly, if you see GaN mentioned for the onboard charger, anticipate more efficient power transfer and less time plugged in. Different technologies bring their unique advantages, and you can feel the benefits with every use. Knowing the differences empowers you to make informed choices.